As the best descriptive term for the resident microbiota is _______. takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Resident microbiota, a complex and dynamic community of microorganisms residing within the human body, plays a pivotal role in maintaining homeostasis and overall health. Understanding the characteristics, composition, and functions of this microbiota is crucial for unraveling its profound impact on human physiology and disease.
Definition of Resident Microbiota
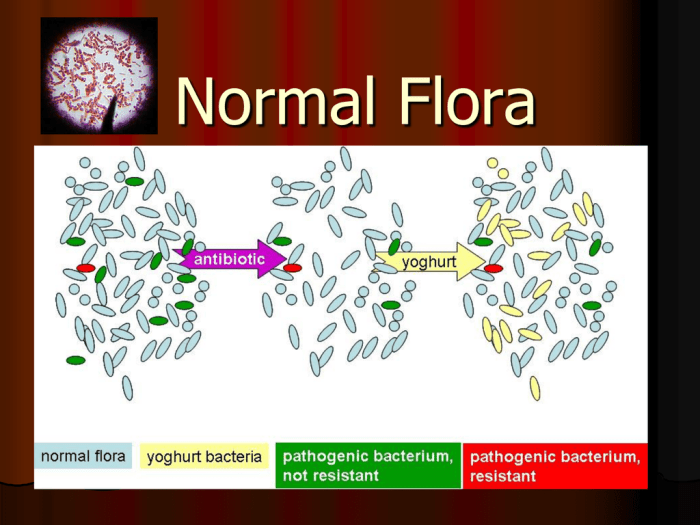
The term “resident microbiota” refers to the community of microorganisms that inhabit a specific niche within the human body and maintain a stable presence over time. These microorganisms, which include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa, play a crucial role in maintaining human health and well-being.
Characteristics of Resident Microbiota
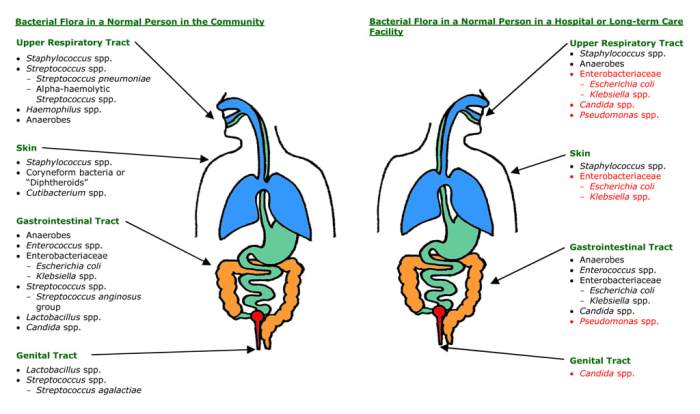
Resident microbiota are characterized by several key features:
- Stability:Resident microbiota maintain a relatively stable composition over time, despite fluctuations in the host’s environment and diet.
- Diversity:Resident microbiota are highly diverse, with a wide range of species and strains present in different niches within the body.
Composition of Resident Microbiota
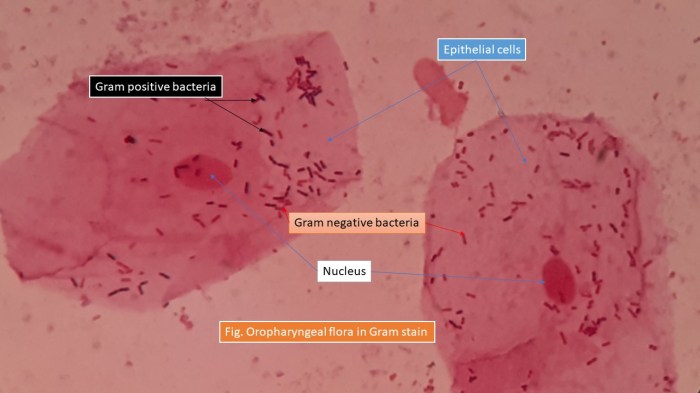
| Body Site | Major Taxonomic Groups |
|---|---|
| Skin | Staphylococcus, Propionibacterium, Corynebacterium |
| Oral cavity | Streptococcus, Lactobacillus, Veillonella |
| Gastrointestinal tract | Bacteroides, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria |
| Urogenital tract | Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Enterobacteriaceae |
The composition of resident microbiota varies significantly across different body sites, reflecting the unique environmental conditions and functions required at each site.
Functions of Resident Microbiota: The Best Descriptive Term For The Resident Microbiota Is _______.
Resident microbiota perform a wide range of essential functions in the human body, including:
- Metabolic functions:Resident microbiota assist in the digestion and absorption of nutrients, produce vitamins, and participate in the detoxification of harmful substances.
- Immune-modulating roles:Resident microbiota interact with the host immune system, stimulating immune responses and protecting against pathogens.
- Protective effects against pathogens:Resident microbiota compete with pathogenic microorganisms for resources, produce antimicrobial substances, and strengthen the host’s physical barriers.
Factors Influencing Resident Microbiota
The composition and function of resident microbiota can be influenced by various factors, including:
- Diet:Diet has a significant impact on the diversity and composition of resident microbiota.
- Lifestyle:Lifestyle factors such as exercise, sleep, and stress can also influence resident microbiota.
- Environmental exposures:Exposure to environmental pollutants, antibiotics, and other chemicals can disrupt the balance of resident microbiota.
Dysbiosis and Resident Microbiota
Dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the composition or function of resident microbiota. Dysbiosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including antibiotic use, poor diet, and chronic diseases. It can lead to a range of health problems, including gastrointestinal disorders, immune dysfunction, and metabolic disturbances.
Strategies for restoring balance to resident microbiota include:
- Probiotics:Probiotics are live microorganisms that can be consumed to improve the balance of resident microbiota.
- Prebiotics:Prebiotics are non-digestible food ingredients that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Dietary modifications:Dietary changes, such as increasing fiber intake and reducing processed food consumption, can support the health of resident microbiota.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of resident microbiota?
Resident microbiota plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including nutrient metabolism, immune system modulation, and protection against pathogens.
How does dysbiosis impact human health?
Dysbiosis, an imbalance in the composition and function of resident microbiota, can contribute to the development of various diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and metabolic disorders.
What factors can influence resident microbiota?
Factors such as diet, lifestyle, and environmental exposures can significantly influence the composition and function of resident microbiota.