Embark on an enlightening journey with Human Evolution Skull Analysis Gizmo Assessment Answers, where the mysteries of our origins unravel. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of skull morphology, function, and adaptation, offering unparalleled insights into the evolutionary tapestry of humankind.
As we explore the nuances of skull shape and size, we uncover the profound implications for understanding the trajectory of human evolution. Discover how natural selection has meticulously sculpted the skull to fulfill its vital functions, providing a testament to the power of adaptation.
1. Skull Morphology Analysis: Human Evolution Skull Analysis Gizmo Assessment Answers
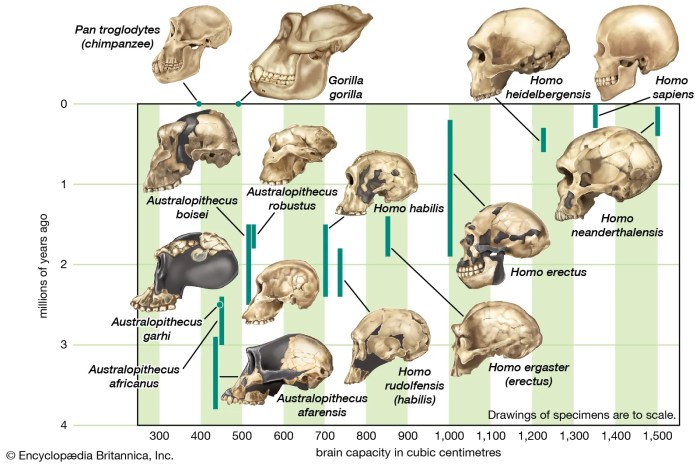
Skull morphology is a critical area of study in human evolution, providing valuable insights into our evolutionary history. The shape and size of the skull have undergone significant changes over time, reflecting adaptations to environmental pressures and functional demands.
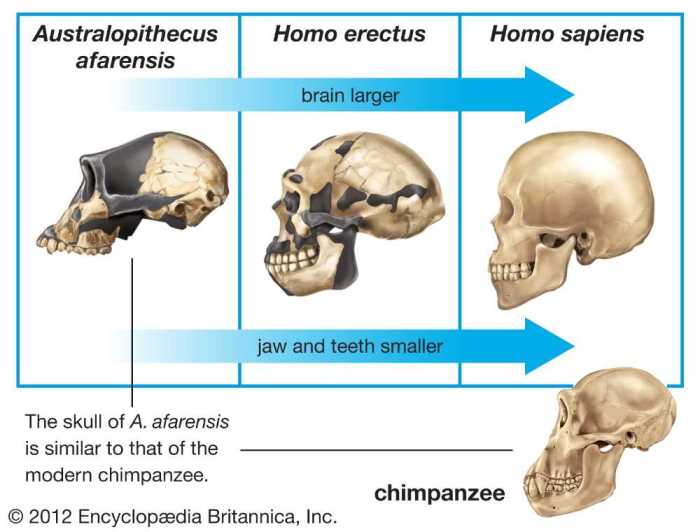
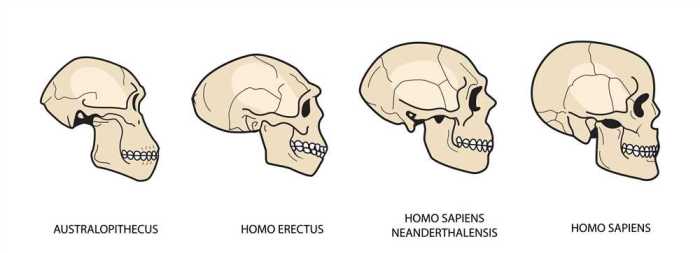
Early hominids, such as Australopithecus afarensis, had relatively small brains and prognathic jaws, indicating a diet primarily consisting of plant material. As hominids evolved into Homo erectus, the skull became larger, with a more upright posture and reduced prognathism, suggesting a shift towards a more omnivorous diet.
The emergence of Homo sapiens brought about further cranial changes, including an even larger braincase, reduced brow ridges, and a more gracile facial structure. These morphological changes are associated with increased cognitive abilities, tool use, and social complexity.
2. Skull Function and Adaptation, Human evolution skull analysis gizmo assessment answers
The skull serves various essential functions in humans, including:
- Protecting the brain from injury
- Supporting the facial muscles and providing a framework for the eyes, nose, and mouth
- Facilitating mastication (chewing) through the attachment of jaw muscles
- Housing the organs of hearing and balance
Over time, the skull has adapted to meet these functions effectively. For instance, the thickening of the skull bones provides increased protection for the brain, while the development of a sagittal crest in some hominid species provides additional support for the jaw muscles.
Natural selection has played a significant role in shaping skull evolution. Individuals with advantageous skull traits, such as larger brain capacity or stronger jaw muscles, were more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their genetic advantages to future generations.
3. Comparative Skull Analysis
Comparative skull analysis involves comparing the skulls of different hominid species to identify key differences in morphology and function. For example, the skull of Homo neanderthalensis exhibits a robust brow ridge, a large nasal cavity, and a projecting occipital bun, suggesting adaptations for cold climates and heavy chewing.
In contrast, the skull of Homo sapiens is characterized by a high forehead, a smaller nasal cavity, and a reduced occipital bun, reflecting adaptations for increased brain size and a more diverse diet.
Such comparative analyses provide valuable insights into the evolutionary relationships between different hominid species and their adaptations to specific environmental niches.
4. Skull as a Tool for Understanding Human Origins
Skull analysis plays a crucial role in understanding human origins. By examining the skulls of early hominids and comparing them to modern humans, researchers can reconstruct our evolutionary history and gain insights into the adaptations that led to our species’ success.
The presence of hominid fossils with intermediate skull features, such as Homo habilis and Homo rudolfensis, provides evidence for the gradual evolution of the human skull over millions of years.
Skull analysis also helps determine the timing and geographic distribution of different hominid species, contributing to our understanding of human migration and dispersal patterns.
FAQ Summary
What is the significance of skull morphology in human evolution?
Skull morphology provides valuable insights into evolutionary changes in brain size, shape, and function, reflecting adaptations to environmental pressures and dietary shifts.
How has skull function adapted to meet the needs of humans?
The skull has evolved to protect the brain, facilitate sensory perception, and support mastication, showcasing the remarkable plasticity of our anatomy.
What role does comparative skull analysis play in understanding human evolution?
By comparing the skulls of different hominid species, we can identify morphological variations that shed light on evolutionary relationships and adaptive strategies.