Introducing Lesson 1.1 Building Blocks of Geometry Answer Key, the ultimate guide to unraveling the foundational concepts of geometry. Embark on an enlightening journey as we explore the intricate world of points, lines, planes, and angles, unlocking the secrets that underpin this fascinating subject.
Delve into the captivating realm of geometry, where precision and clarity reign supreme. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the fundamental principles, empowering you with a deep understanding of the building blocks that shape our physical world.
Lesson 1.1 Building Blocks of Geometry Answer Key
Lesson 1.1 of Building Blocks of Geometry provides an overview of the fundamental concepts in geometry, including points, lines, planes, and angles. It establishes the foundation for understanding more complex geometric shapes and their properties.
Points, Lines, and Planes, Lesson 1.1 building blocks of geometry answer key
A point is a location in space that has no dimensions. A line is a one-dimensional object that extends infinitely in both directions. A plane is a two-dimensional object that extends infinitely in all directions.
Points, lines, and planes are the building blocks of geometry. They are used to create more complex geometric shapes, such as triangles, squares, and circles.
| Characteristic | Point | Line | Plane |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Shape | No shape | Straight | Flat |
| Length | No length | Infinite | Infinite |
| Width | No width | No width | Infinite |
Angles
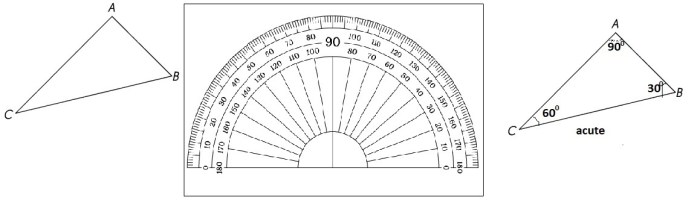
An angle is formed when two lines meet. Angles are measured in degrees. A right angle measures 90 degrees, an acute angle measures less than 90 degrees, and an obtuse angle measures greater than 90 degrees.
Angles are important in geometry because they are used to determine the properties of geometric shapes.
Angle Relationships
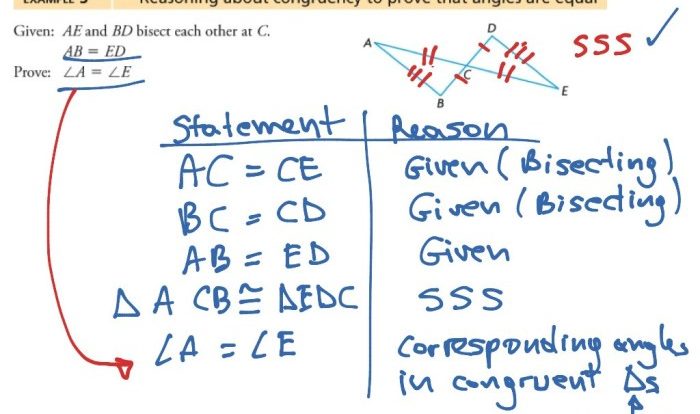
Angles can be related to each other in different ways. Complementary angles add up to 90 degrees, supplementary angles add up to 180 degrees, and vertical angles are equal.
Angle relationships are important in geometry because they can be used to solve problems and to determine the properties of geometric shapes.
| Angle Relationship | Definition |
|---|---|
| Complementary angles | Two angles that add up to 90 degrees |
| Supplementary angles | Two angles that add up to 180 degrees |
| Vertical angles | Two angles that are opposite each other and have the same measure |
Geometric Figures
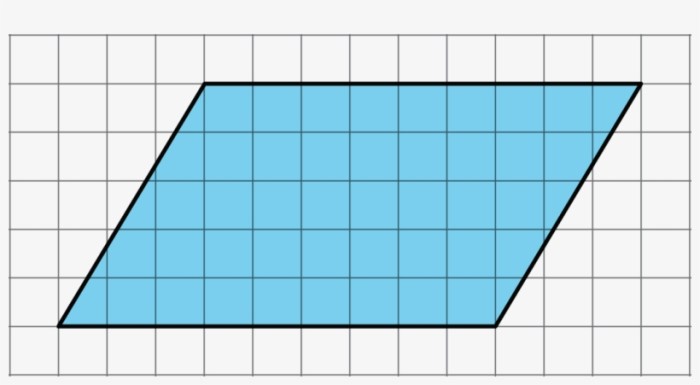
Geometric figures are two-dimensional shapes that are defined by their sides and angles. Common geometric figures include triangles, squares, and circles.
Geometric figures are important in geometry because they are used to create more complex geometric shapes and to solve problems.
Applications of Geometry
Geometry is used in a variety of fields, including architecture, engineering, and art. Geometry is used to design buildings, bridges, and other structures. It is also used to create art and to solve problems in science and engineering.
Geometry is a fundamental branch of mathematics that has many applications in the real world.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the key concepts covered in Lesson 1.1?
Lesson 1.1 covers the fundamental concepts of geometry, including points, lines, planes, and angles.
How are angles measured?
Angles are measured in degrees, with a full circle measuring 360 degrees.
What are the different types of geometric figures?
Geometric figures include triangles, squares, circles, and many more, each with its unique properties and characteristics.