A solution with a pH of 3.6 would be mildly acidic, with a higher concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) than hydroxide ions (OH-). This acidic nature imparts unique chemical properties and practical applications to such solutions, making them valuable in various fields.
This article delves into the intricacies of solutions with a pH of 3.6, exploring their chemical characteristics, discussing their applications, and emphasizing the safety considerations associated with handling acidic solutions.
Understanding pH and Acidic Solutions
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the hydrogen ion concentration in moles per liter (mol/L).
Acidity and alkalinity are two opposite ends of a spectrum. Acidic solutions have a pH less than 7, while alkaline solutions have a pH greater than 7. A pH of 7 is considered neutral.
Range of pH Values and their Implications
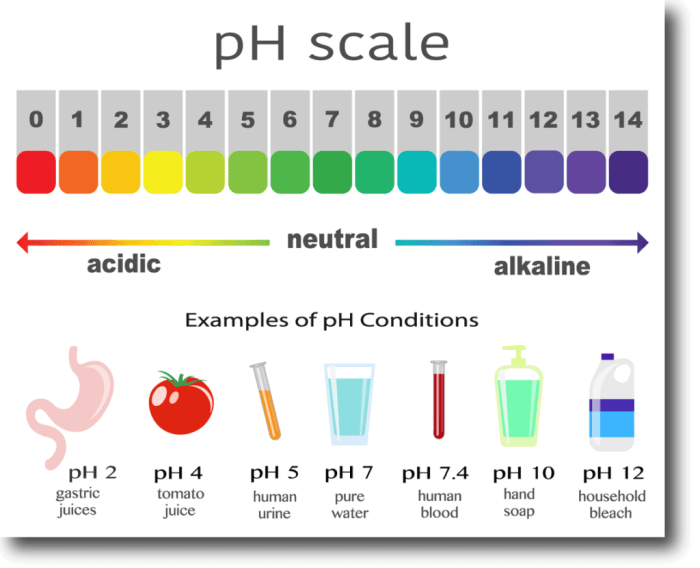
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14.
- pH 0-6: Strongly acidic
- pH 6-7: Weakly acidic
- pH 7: Neutral
- pH 7-8: Weakly alkaline
- pH 8-14: Strongly alkaline
The pH of a solution can have a significant impact on its chemical properties and biological processes.
Chemical Properties of Solutions with pH 3.6

Solutions with a pH of 3.6 exhibit distinct chemical properties that stem from their acidic nature. Understanding the presence and behavior of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) is crucial in comprehending the chemical reactivity of these solutions.
Presence of Hydrogen and Hydroxide Ions
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity. A pH below 7 indicates an acidic solution, and a pH of 3.6 falls within this range. In acidic solutions, the concentration of H+ ions exceeds that of OH- ions.
In the case of a pH of 3.6, the H+ ion concentration is 10 -3.6moles per liter (M), while the OH- ion concentration is 10 -10.4M.
Acidic Nature of Solutions with pH below 7
The presence of a higher concentration of H+ ions in solutions with a pH below 7 imparts an acidic character to these solutions. Acidic solutions react with certain substances, such as metals and bases, to produce salts and water. They also turn blue litmus paper red and have a sour taste.
Applications of Acidic Solutions with pH 3.6

Acidic solutions with a pH of 3.6 have numerous applications in various fields, primarily due to their acidic nature. The acidity of these solutions plays a crucial role in specific processes and reactions, making them valuable in various industrial, scientific, and everyday applications.
One of the key applications of acidic solutions with a pH of 3.6 is in the food and beverage industry. These solutions are commonly used as preservatives in food products to inhibit the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms that can cause spoilage.
The acidic environment created by these solutions helps extend the shelf life of food items, ensuring their safety and quality.
Food Preservation, A solution with a ph of 3.6 would be
- Acidic solutions with a pH of 3.6 are commonly used as preservatives in food products to inhibit the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms that can cause spoilage.
- The acidic environment created by these solutions helps extend the shelf life of food items, ensuring their safety and quality.
- Examples of food products that utilize acidic solutions as preservatives include pickles, sauerkraut, and vinegar-based condiments.
Safety Considerations and Handling
Acidic solutions, like the one prepared with a pH of 3.6, pose certain hazards that require careful handling and safety precautions. These solutions can cause skin irritation, burns, and eye damage if not handled properly.
Storage and Handling
Acidic solutions should be stored in corrosion-resistant containers and kept tightly sealed to prevent spills and leaks. Storage areas should be well-ventilated to minimize exposure to fumes and vapors. Handling these solutions should be done while wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat.
Disposal
Proper disposal of acidic solutions is crucial to protect the environment and human health. Neutralization is often necessary before disposal, which can be achieved by slowly adding a base to the acidic solution until a neutral pH is reached. The neutralized solution can then be disposed of according to local regulations.
Personal Protective Equipment
Wearing appropriate PPE is essential when handling acidic solutions. Gloves made of nitrile or neoprene provide protection against skin contact, while goggles or a face shield protect the eyes from splashes and vapors. A lab coat prevents spills from reaching clothing and skin.
Proper Handling Techniques
Handling acidic solutions requires careful techniques to minimize risks. Always handle these solutions in a fume hood or well-ventilated area. Avoid splashing or spilling, and never mix concentrated acids with other chemicals unless specifically instructed to do so. If contact with skin or eyes occurs, flush the affected area immediately with plenty of water and seek medical attention if necessary.
FAQ Corner: A Solution With A Ph Of 3.6 Would Be
What is the significance of pH in chemistry?
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, indicating the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+). It plays a crucial role in determining the chemical behavior and reactivity of substances.
What safety precautions should be taken when handling acidic solutions?
When handling acidic solutions, it is essential to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and a lab coat. Proper ventilation and careful handling techniques are also crucial to minimize exposure to acidic fumes and potential skin irritation.